Introduction to Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
In recent years, electric vehicles (EVs) have surged in popularity, largely due to an increased awareness of environmental issues and advancements in technology. As this trend continues, electric vehicle charging stations have become a vital component in facilitating the adoption of electric mobility. These stations offer a necessary service, ensuring that EV users have convenient access to charging options, which in turn supports the shift away from traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
Electric vehicle charging stations function by delivering electricity from the grid to the vehicle’s battery, allowing users to recharge their vehicles’ power supply. This process is essential for those who rely on electric mobility, as it enables them to cover longer distances without the anxiety of battery depletion. Charging stations vary in terms of power output and charging speed, which significantly impacts the overall charging experience.
There are primarily three types of EV charging stations: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Chargers. Level 1 chargers utilize a standard household outlet and are typically the slowest, making them suitable primarily for home use. Level 2 chargers offer a quicker charging solution, often found in public locations such as shopping centers and workplaces. In contrast, DC Fast Chargers are specifically designed for rapid charging, allowing EVs to recharge to substantial battery levels in a fraction of the time required by the other types.
Ultimately, the presence of various charging station types ensures that EV users can find suitable charging options tailored to their needs. The strategic deployment of these stations across urban and rural landscapes will further promote electric mobility, alleviate range anxiety, and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future. A robust network of electric vehicle charging stations is essential for the widespread acceptance and utilization of electric vehicles.
Types of EV Charging Stations
Electric vehicles (EVs) require efficient charging solutions, and understanding the different types of EV charging stations is essential for users. The primary classifications include Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging stations, each serving distinct purposes based on voltage and charging speed.
Level 1 charging stations typically use a standard 120-volt outlet, making them the most accessible option for home charging. This form of charging produces around 4 to 5 miles of range per hour, which suits drivers who can leave their EVs plugged in overnight. Although Level 1 stations may be less efficient for long-distance drivers, they are ideal for daily commutes and slow, overnight charging at home.
Level 2 charging stations operate at a higher voltage of 240 volts, allowing for a significantly shorter charging time compared to Level 1. These stations can provide between 10 to 60 miles range per hour of charging, depending on the vehicle’s compatibility and the charger’s power output. Level 2 stations are commonly found in public charging locations, workplaces, and residential areas, making them suitable for both short stops and extended parking sessions. They balance convenience and efficiency, making them popular among EV owners.
DC Fast Charging stations are the most advanced, capable of delivering rapid charging for electric vehicles. Operating at 480 volts, these stations can recharge an EV to 80% in as little as 30 minutes, a significant advantage for long-distance travel. However, they are limited to DC-compatible vehicles and are typically located along highways or in strategic urban locations to facilitate quick recharges during road trips. Understanding these three types of EV charging stations is crucial for EV owners to optimize their charging needs effectively.
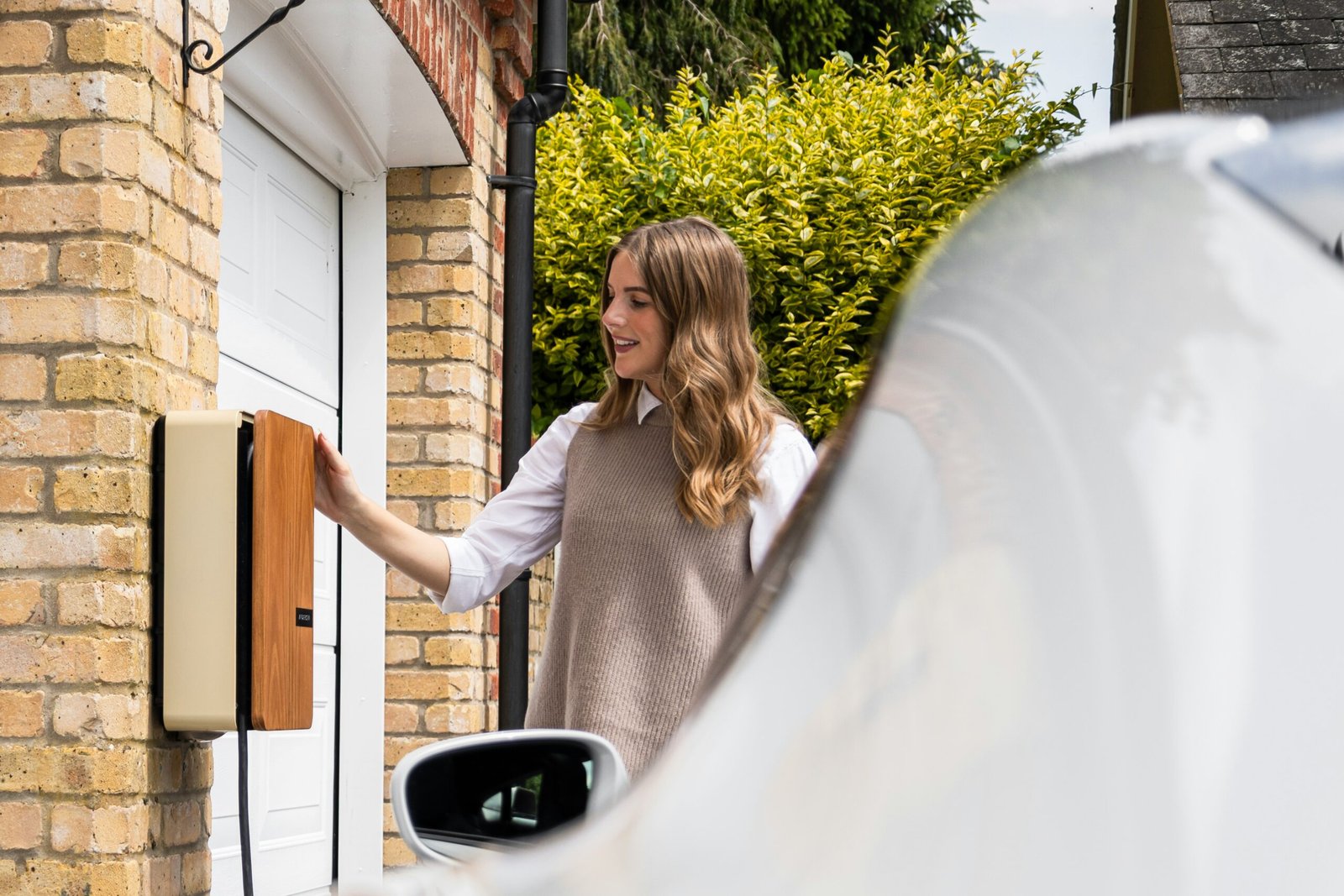
Home EV Charging: Installation and Costs
Installing a home electric vehicle (EV) charging station provides several advantages for EV owners, most notably the convenience of charging your vehicle overnight. The process typically involves the installation of a Level 2 charging station, which requires a dedicated 240-volt outlet. Unlike a standard Level 1 charger that draws from a regular 120-volt outlet, a Level 2 charger significantly reduces the charging time, allowing drivers to utilize their EVs more efficiently.
The installation process usually begins with an assessment of the existing electrical system in the home. A licensed electrician will evaluate the capacity of the household’s electrical panel and determine if any upgrades are necessary. Depending on the home’s current infrastructure, these upgrades may include enhancing the amperage capacity of the panel or adding a new circuit dedicated to the EV charger. Homeowners should expect to invest between $500 and $3,000 for installation, largely dependent on the complexity of the electrical work required and the cost of the charging unit itself.
In addition to installation costs, it is prudent to consider potential incentives or rebates that can offset these expenses. Various federal, state, and local programs may provide financial assistance to homeowners installing EV chargers, aimed at promoting sustainable transportation. For instance, the federal tax credit may cover a percentage of the costs incurred during both the purchase and installation of a home charging station. Furthermore, some utility companies offer rebates for energy-efficient upgrades, which can include EV chargers.
Ultimately, the benefits of having a dedicated EV charging station at home extend beyond convenience. It can lead to cost savings through lower electricity rates during off-peak hours and increase the overall property value. With the rise of electric vehicles and the expanding network of charging infrastructure, investing in a home EV charging station represents a forward-thinking option for many homeowners.
Public Charging Infrastructure: Overview and Locations
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, the expansion of public charging infrastructure has become increasingly critical in facilitating their adoption. Public charging stations are designed to provide convenient access to charging facilities for EV owners, particularly for those who do not have the option to charge at home. These stations can be found in various locations, including shopping centers, parking garages, office buildings, and along highways, ensuring a network that supports extensive travel routes.
To locate public charging stations efficiently, several resources are available. Numerous mobile applications and websites, such as PlugShare and ChargePoint, provide up-to-date information on charging locations and availability. These platforms often include user reviews and real-time updates, allowing drivers to make informed decisions about charging stops. Additionally, many EV manufacturers incorporate navigation systems that direct users to the nearest charging stations, enhancing the overall charging experience.
The role of charging networks is pivotal in the public charging ecosystem. Companies such as Electrify America, Ionity, and Tesla have established extensive charging networks, offering fast and reliable charging options across different regions. These networks not only provide varying charging speeds but also ensure compatibility with multiple EV models, addressing concerns about range anxiety among potential EV owners. As demand for EVs grows, charging networks are actively working to expand their infrastructure, particularly in urban areas where the concentration of vehicles is highest.
The growth of public charging infrastructure is expected to continue, driven by both technological advancements and increasing governmental support. Urban areas are particularly poised for growth, as local governments and private enterprises collaborate to install more charging stations. This ongoing development is crucial in supporting the transition to electric mobility and meeting the rising expectations of consumers for accessible and convenient charging solutions.
Comparing Costs: Home Charging vs. Public Charging
When considering the expenses associated with electric vehicle (EV) charging, it is essential to compare the costs associated with home charging and public charging. Home charging typically entails utilizing a Level 2 charging station installed in the owner’s garage or a designated parking area. The primary cost associated with this option is the electricity consumed during the charging process. In the United States, the average residential electricity rate hovers around $0.13 to $0.15 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). For instance, charging a standard EV with a 60 kWh battery from empty to full would cost approximately $7.80 to $9.00, depending on local rates.
In contrast, public charging stations offer varying fee structures that can significantly impact the overall charging costs for EV owners. Many public charging locations charge per session or per kWh. Additionally, these stations often implement transaction fees, which can range from a flat fee of around $1 to several dollars depending on the provider and charging speed. Rapid chargers, for example, may charge a premium price, reflecting their faster charging capability. Furthermore, financial incentives such as membership programs or promotional prices can influence overall costs at public stations.
Additional factors also affect the choice between home and public charging, including convenience, availability, and personal driving habits. While home charging is generally more economical, it requires access to a power outlet and the installation of a charging unit. In contrast, public charging provides flexibility for those who may not have access to home charging or who are on long road trips. Ultimately, the decision will depend on the individual’s lifestyle and driving patterns, alongside a careful consideration of these cost factors.
Charging Etiquette and Best Practices
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, understanding the etiquette surrounding public charging stations becomes increasingly important. Proper charging station etiquette not only ensures a smooth experience for all users but also cultivates a sense of community among EV drivers. First and foremost, it is essential to be aware of your charging time. Most charging stations will indicate the duration of the charging session, which usually varies based on the type of charger being used. Be mindful of these time limits and make an effort to unplug once your vehicle has reached an adequate charge level, especially during peak hours when demand may be high.
Moreover, sharing resources at charging stations can contribute to an efficient charging experience. If your vehicle is fully charged and other drivers are waiting, promptly vacating the parking space is a crucial aspect of responsible charging behavior. This simple act of consideration can significantly reduce wait times and promote goodwill among fellow EV users. In addition to unplugging when a charge is complete, consider carpooling whenever possible or traveling during off-peak hours to lessen congestion at popular charging locations.
It is also important for EV drivers to communicate effectively. Use discretion when discussing charging needs with others, and feel free to offer assistance to fellow drivers who might be experiencing difficulties. Many charging stations feature a mix of Level 2 and Level 3 chargers; understanding the various charging levels can help in selecting the right station for your needs without monopolizing the resource.
Ultimately, being courteous to other EV drivers helps strengthen the EV community. By adopting these best practices for charging etiquette, you contribute to a more collaborative and supportive environment that enhances the overall EV experience for all users.
Future Trends in EV Charging Technology
The electric vehicle (EV) market is evolving rapidly, and with it, the technology behind EV charging stations is advancing to meet the growing demand for efficient, accessible, and sustainable energy solutions. One of the most exciting developments on the horizon is wireless charging. This technology enables vehicles to charge without being physically connected to a power source, using inductive charging pads embedded in roads or parking spots. This innovation not only offers greater convenience for EV drivers but also holds the potential to alleviate charging time concerns, making electric vehicles more appealing to a broader audience.
Another significant trend is the emergence of ultra-fast chargers. With charging times potentially reduced to as little as 15 to 30 minutes, ultra-fast charging stations are becoming a critical component of the EV infrastructure. These high-powered chargers are designed to deliver substantial energy quickly, catering to the needs of drivers who may be pressed for time. As electric vehicle production scales up, the deployment of these stations will be crucial to maintaining the momentum of EV adoption.
Solar-assisted charging is also gaining traction as a sustainable solution to EV charging. By harnessing solar energy, these charging stations can provide renewable energy to charge EVs, reducing the reliance on grid electricity. This dual benefit not only supports environmental goals but also offers cost savings for users. Furthermore, the integration of smart grid technology is set to enhance charging infrastructure significantly. Smart grids can optimize energy distribution and manage charging loads, ensuring that EV users have access to charging stations even during peak demand periods. This integration will not only improve user experience but also contribute to grid stability.
As these trends unfold, they represent a significant shift towards making electric vehicles more practical and accessible. The advancements in charging technology not only address current limitations but also pave the way for a more robust and user-friendly EV ecosystem.
Regulatory Landscape and Incentives for EV Charging
The regulatory landscape surrounding electric vehicle (EV) charging stations is evolving as governments strive to promote sustainable transportation. Various initiatives at federal, state, and local levels are designed to foster the development of charging infrastructure and increase accessibility for EV owners. This push towards electrification is not only beneficial for the environment but also aims to stimulate economic growth. One significant federal initiative is the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which allocates funds specifically for the construction and expansion of EV charging stations across the United States.
At the federal level, tax credits have been introduced to encourage both individuals and businesses to invest in EV charging equipment. The Federal Electric Vehicle Charging Station Tax Credit offers a 30% tax credit on the purchase and installation of EV chargers, thereby reducing the overall financial burden on consumers and businesses. Additionally, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) provides grant opportunities aimed at expanding public charging infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas.
State and local governments also play a critical role in fostering a favorable regulatory environment for EV charging. Many states have established their own incentives—such as rebates, tax credits, and grants—to motivate homeowners and businesses to install charging stations. For example, California, known for its ambitious climate goals, offers substantial rebates through its Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Project (EVIP), which particularly supports low-income communities. Similarly, some states have enacted laws mandating that new buildings include EV charging capabilities, ensuring that future infrastructure can accommodate the growing number of electric vehicles on the road.
Overall, the landscape for EV charging regulation and incentives is dynamic and multifaceted, reflecting a commitment to expanding the use of electric vehicles. By providing financial incentives and fostering supportive policies, governmental bodies are facilitating the essential transition toward a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for EV Charging Stations
As we navigate the future landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), the significance of comprehensive charging infrastructure cannot be overstated. The adoption of electric vehicles is intricately linked to the availability and efficiency of EV charging stations. This infrastructure not only facilitates the convenience and practicality of owning an EV but also enhances consumer confidence, which is crucial for broader acceptance of electric mobility.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the various types of EV charging stations, ranging from Level 1 chargers, which provide a slower charge ideal for residential use, to Level 3 fast chargers designed for quick top-ups during long journeys. Understanding the distinctions among these charging options is vital, as it informs consumers about the best solutions tailored to their specific needs. Moreover, the costs associated with installing and using these charging stations presented a practical consideration for prospective EV owners and business operators alike. Addressing the economic implications will play an essential role in fostering a more widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Furthermore, the influence of policymakers in shaping the future framework of EV charging stations is a pivotal aspect. Incentives, regulations, and investments in sustainable energy initiatives are essential for developing a robust charging network. Collaboration among manufacturers, consumers, and government entities is crucial in revolutionizing the EV market. As individuals increasingly opt for electric vehicles, it is imperative for stakeholders to consider infrastructure enhancements that can adapt to growing demand.
In conclusion, as we stand on the brink of a transformative shift towards electric mobility, fostering a persistent dialogue regarding the evolution of EV charging stations will ensure a smoother transition. This will, in turn, promote both environmental sustainability and economic viability, paving the way for a cleaner, more energy-efficient future.